Table of Contents
- Difference Between RGB & CMYK Colors
- What Is RGB Color Mode?
- What Is CMYK Color Mode?
- Main Differences Between RGB and CMYK
- Advantages of RGB colors
- Advantages of CMYK colors
- FAQ: CMYK & RGB Colors:
Difference Between RGB & CMYK Colors
Color plays a powerful role in how we perceive design, branding, and visual communication. Whether you’re creating a website, designing a logo, or printing marketing materials, choosing the correct color mode is essential. Two of the most commonly used color models are RGB and CMYK. Despite their initial similarities, they have quite diverse functions. Understanding the difference between RGB and CMYK colors can save time, money, and frustration—especially when transitioning between digital and print designs.
What Is RGB Color Mode?
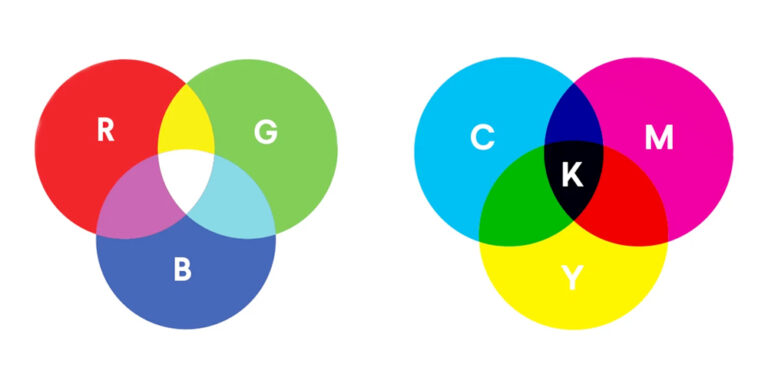
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue. It is an additive color model, meaning colors are created by adding light together. This color mode is used primarily for digital screens, such as computers, smartphones, tablets, televisions, and cameras.
In the RGB model, colors are formed by combining varying intensities of red, green, and blue light. White is the outcome of combining all three hues at maximum intensity. Black is the outcome when there is no light.
Key Features of RGB
- Designed for screens and digital displays
- Uses light to create color
- Produces bright and vibrant colors
- Larger color range (gamut) compared to CMYK
- Common formats: RGB, sRGB, Adobe RGB
RGB is ideal for web design, social media graphics, videos, mobile apps, and any content that will be viewed on a screen.
What Is CMYK Color Mode?
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black). It is a subtractive color model, which means colors are created by subtracting light through ink absorption. CMYK is used primarily in printing, including brochures, business cards, magazines, packaging, and posters.
In CMYK printing, colors are created by layering ink on paper. As more ink is added, more light is absorbed, resulting in darker colors. Combining cyan, magenta, and yellow theoretically creates black, but due to ink impurities, black ink (K) is added to achieve deeper and more accurate shadows.
Key Features of CMYK
- Designed for printed materials
- Uses ink, not light
- Produces more muted and realistic colors
- Smaller color range than RGB
- Standard for commercial printing

Main Differences Between RGB and CMYK
- Purpose and Usage: The biggest difference between RGB and CMYK lies in where they are used. RGB is meant for digital displays, while CMYK is intended for print. Using the wrong color mode can lead to unexpected results, especially when printing digital designs.
- Color Creation Method: RGB creates colors by adding light, while CMYK creates colors by subtracting light using ink. This fundamental difference affects how colors appear in each mode.
- Color Brightness: RGB colors appear brighter and more vivid because screens emit light. CMYK colors tend to look duller because ink absorbs light. Neon and highly saturated colors often cannot be accurately reproduced in CMYK.
- Color Gamut: RGB can display more colors than CMYK because of its larger color gamut. Some colors visible on a screen simply cannot be printed using CMYK inks.
- Black and White Representation: In RGB, white is created by combining all colors at full intensity, while black is the absence of light. In CMYK, white is the natural color of paper, and black is produced using black ink.
Advantages of RGB colors
- Ideal for digital displays: RGB (Red, Green, Blue) is designed for screens like TVs, monitors, smartphones, and cameras, which emit light using these three colors.
- Wide range of colors: By mixing red, green, and blue at different intensities, RGB can produce millions of colors, enabling rich and vibrant visuals.
- Accurate color reproduction on screens: Since screens are built around RGB technology, this model gives more accurate and consistent color output for digital content.
- Easy color manipulation: Colors can be adjusted simply by changing numerical RGB values (0–255), making it convenient for designers and developers.
- Supports brightness control: RGB directly controls light intensity, allowing smooth changes in brightness and contrast.
- Standard for digital media: Most image formats (JPEG, PNG), design tools, and programming environments use RGB as the default color model.
- Efficient for graphics and animations: RGB works well with GPUs and digital processing, making it efficient for games, videos, and animations.
Advantages of CMYK colors
- Best for printing
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black) is specifically designed for printed materials like books, magazines, posters, and packaging. - Accurate print color output
Printers use CMYK inks, so designs made in CMYK closely match the final printed result. - Cost-effective printing
CMYK uses standard inks and is more economical than special color systems for large-scale printing. - Better control of ink usage
The black (K) ink improves depth and detail while reducing the need to mix large amounts of color ink. - Consistent color reproduction
CMYK ensures uniform colors across multiple print runs when calibrated properly. - Industry standard for print media
Most professional printing presses and design software are optimized for CMYK workflows. - Improved text clarity
Black ink produces sharper and cleaner text compared to mixing cyan, magenta, and yellow. - Suitable for a wide range of materials
CMYK works well on paper, cardboard, labels, brochures, and other physical surfaces.
FAQ: CMYK & RGB Colors:
1. What is RGB color mode?
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue. It is a color model used in digital screens where colors are created by mixing light.
2. Where is RGB used?
RGB is used in monitors, televisions, smartphones, cameras, websites, videos, and digital graphics.
3. What is CMYK color mode?
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black (Key). It is a color model used in printing that works by absorbing light through ink.
4. Where is CMYK used?
CMYK is used in printers, magazines, brochures, posters, newspapers, and packaging materials.
5. What is the main difference between RGB and CMYK?
- RGB is an additive color model (adds light)
- CMYK is a subtractive color model (subtracts light using ink)